note Note générale
Risk management: FabMob Qc focuses on prevention and proactivity
Founded in 2018 to implement technological commons in sustainable mobility, La Fabrique des Mobilités Québec is a nonprofit whose mission is to mobilize players in the Quebec ecosystem to experiment with and mitigate risks relating to sustainable mobility approaches and solutions. FabMob Qc is actively involved in the promotion of mobility data, particularly in Montreal.
Parking planners, geolocated traffic signs, and curb management are just some of the topics tackled by this Quebec center of excellence in sustainable mobility. FabMob Qc has also launched the development of an open source mobility data collection app, Ma Mobilité.
The FabMob QC team was faced with new data governance challenges and issues related to their mobile app. This case study details the reflections, tools and processes that stemmed from the targeted coaching provided by Open North and led to improved data governance for the Ma Mobilité app.
Data management and security are a priority for FabMob Qc. The nonprofit is deeply committed to protecting its app users. Through the coaching sessions, FabMob Qc's objective was to optimize its data governance to guarantee the safety of both data and application users.

Do you face similar challenges in your own organization?
Explore FabMob Qc's experiments and reflections as part of the targeted coaching.
Mobility app and risk management
During the targeted coaching sessions, the FabMob Qc team looked at the risks associated with users’ usage of the mobile app. Here are the key questions that were at the heart of this process:
- Risk identification - What security flaws, vulnerabilities and technical weaknesses are present in the code?
- Risk assessment - What is the level of associated risk, in terms of probability and severity?
- Risk management - What needs to be prioritized, and what approach should be adopted to manage it effectively?
- Compliance with Bill 25 - Have all the necessary steps been taken to comply with the legal standards and provisions put in place by the Quebec government to protect the privacy of Quebec residents?
Risk inventory
The FabMob Qc team's first step was to draw up as exhaustive a list as possible of the risks they faced. This exercise very quickly showed its limitations, as it was difficult to base the list solely on the risks perceived by the team. These initial efforts were soon supplemented by a literature search to enhance the list.
Learning about the Center for Internet Security's (CIS) Critical Security Control Matrix was a turning point in the coaching process. The document provided a recognized, standardized list of vulnerabilities that went beyond the technical dimension. However, in its original state, this document was not suited to the Ma Mobilité app.
A third stage followed, in which FabMob Qc adapted this matrix to their own circumstances, in order to accurately assess the risks associated with their app. The risks identified were classified according to asset type (devices, applications, data, network, or users), dimension (legal, organizational, or technological), security function (detect, identify, protect, react, recover), risk level and mitigation solutions. The risk level was assessed using a risk matrix, a common practice in many fields. This matrix assigns a risk level according to the severity and probability of each event.
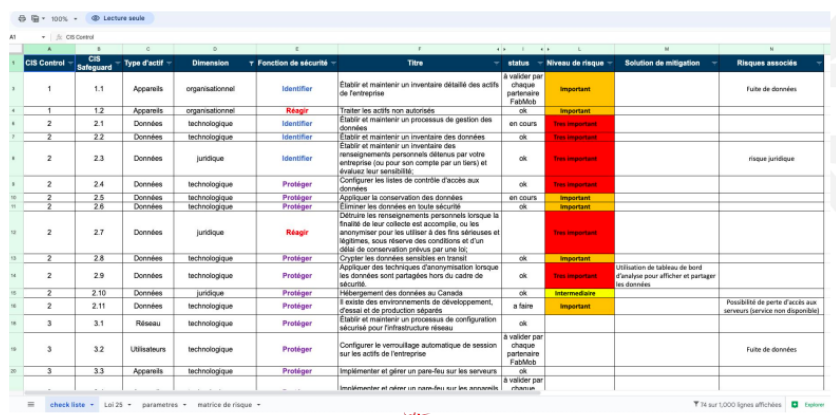
At the end of the coaching, FabMob Qc was able to produce a first draft of a roadmap in order to fine-tune and iterate the exercise effectively.
- Create a list of risks and classify them by degree of importance;
- Define action priorities according to the degree of importance of potential vulnerabilities;
- Measure the effort required to mitigate each vulnerability;
- Highlight the potential risks of not applying certain measures (or best practices) identified in the table;
- Create a document listing best practices, their category, importance and state of application within the project.
Lessons learned from FabMob Qc's work with Open North
- Implementing best practices is easier than identifying risks
It proved simpler to start by establishing best practices and control procedures, and then use these as a basis for identifying risks. This "reverse-engineering" approach enabled the design of data governance-related actions such as managing data storage and access, setting up archiving procedures, and more, to ensure comprehensive and effective data governance. - Data governance cannot be implemented in a vacuum
Data governance requires organization-wide planning, involving ongoing commitment beyond individual projects. Prioritization of roles and responsibilities is crucial in this process. A thorough understanding of how the organization works is essential for effective data governance integration, requiring flexibility to adapt organizational practices to data governance best practices. - Risk management related to data governance extends beyond the data itself
Cybersecurity must encompass elements such as devices, servers and users. This approach incorporates a variety of strategies, from communication and training, to the definition and implementation of procedures, and the use of security tools. This emphasizes that the application of best practices must be holistic to ensure effective data governance.
- Preventive measures to strengthen data security
When it comes to app security and data governance, highlighting the benefits of preventive measures is of crucial importance. Although risk management may not immediately translate into tangible results, the focus is placed on preventing problems from occurring in the first place. Implementing proper data governance remains unquestionably critical for organizations, even if the tangible benefits of prevention can be difficult to measure. The consequences of a security breach can be considerable for an organization; ranging from loss of trust to financial repercussions, leakage of sensitive information, and even legal sanctions.
All in all, the benefits of the targeted coaching are numerous:
- Effective mobilization of the team, with time and resources being devoted to the subject matter
- Identification of all risks (not just technical ones)
- Creation of a checklist
- Clear identification of what can and must be done to minimize risk
- Strong communication to the organization about what needs to be done
Integrating data governance into the organization's culture
As FabMob Qc has progressed with data governance, the team has come to the realization that this approach is not limited to a specific project, and requires a global vision. During the discussions around the Ma Mobilité project, the organization realized that risk management involves exploring many aspects, from source code to team structure. It is therefore necessary to think beyond individual projects.
"Open North's targeted coaching allowed us to establish informed communication throughout the organization, therefore helping to persuade other team members to commit to the process of improving data governance," - Raouf Sadeddine, Strategic Advisor, Mobility.
The resources in the targeted support guide enabled the team to implement best practices with regard to information security, and solidify a categorization of risks.
It's not too late for you to rethink your data governance, too! Check out our other case studies for tips and tricks on improving data governance.
About the Montréal in Common Data Governance Workstream
As the lead of the Data Governance Workstream within Montréal in Common, Open North proposes a data governance journey to the innovation community in order to progressively operationalize the principles of the City of Montreal's Digital Data Charter. The program explicitly focuses on collecting, sharing and leveraging data to inform collective and individual decision-making.
Montréal in Common brings together an innovation community led by the City of Montréal, whose partners are experimenting with solutions in food access, mobility and municipal regulations in a desire to rethink the metropolis. Thirteen projects are being implemented as part of Montréal in Common thanks to the $50 million prize awarded to the city by the Government of Canada as part of the Smart Cities Challenge.
Did you like this blog post? Would you like to know more about data governance? Not sure where to start? Find other resources, free training courses and more on our website: https://opennorth.ca/
Author : Open North
Research and editorial contributions: Jérémy Diaz, Judith François-Langevin and Raouf Sadeddine (FabMob Qc)
We extend our thanks to all our partners and clients, whose work continuously expands and evolves our understanding of data governance and its best practices.
Carnet(s) relié(s)
 file_copy
12 notes
file_copy
12 notes
Data Governance Case Studies
file_copy 12 notes file_copy
33 notes
file_copy
33 notes
Chantier de la gouvernance des données de Montréal en commun
file_copy 33 notesAuteur·trice(s) de note
Contacter les auteur·trice(s)Communauté liée
Montréal en commun
Plus d’informationsPublication
21 mai 2024
Modification
12 juin 2024 10:50
Visibilité
public
Pour citer cette note
Nord Ouvert, Carole Philibien, Fabrique Des Mobilités Québec. (2024). Risk management: FabMob Qc focuses on prevention and proactivity. Praxis (consulté le 13 juillet 2024), https://praxis.encommun.io/n/zCgv-1CLG2eQ_SQOPdhMsk5xltU/.
shareCopier

